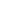About Hunterase
What is
Hunterase?
Composition
Active ingredient : Idursulfase-β 6.0 mg (3 ml in 1 vial)Indication
Hunterase (Idursulfase-β) is indicated for patients with Hunter Syndrome (Mucopolysaccharidosis II, MPS II) as an enzyme replacement therapy (ERT).Who developed
Hunterase?
GC Biopharma is one of the top 5 pharmaceutical companies in Korea that has developed vaccines, plasma derivatives, Drugs for Rare Diseases, and other pharmaceutical products.
Clinical Trials
A 24-week, randomized, single-blind, active comparator-controlled phase I/II trial was conducted in 31 patients with MPS II (6-35 years) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Hunterase in the treatment of MPS II.
Study groups
Primary endpoint
The extent of reduction in urinary GAG excretion.Results
Urine GAG excretion
Patients in all three groups exhibited reduction in urine GAG.
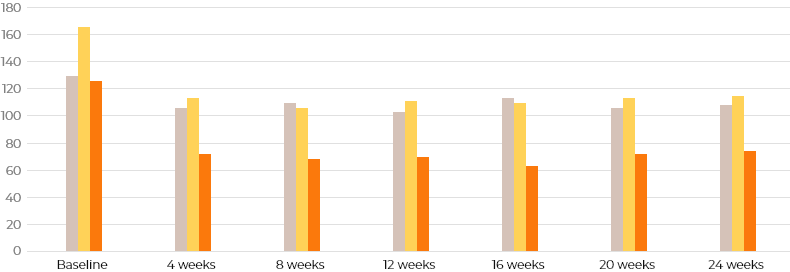
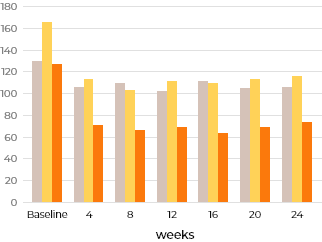
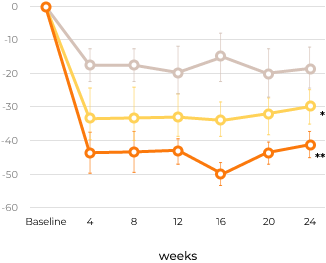
Percent change in urinary GAG excretion
The reduced urine GAG level was maintained throughout the 24 weeks of treatment.
Secondary Endpoints and Results
Secondary endpoints
- 6MWT: the distance walked in 6 minutes
- Pulmonary function test (FVC): forced vital capacity
- Cardiac evaluations (LVMI): left ventricular mass index
- Cardiac evaluations (LVEF): left ventricular ejection fraction
- Joint mobility (joint range of motion): flexion and extension of the shoulder, elbow, hip, and knee
Results
Percent change in 6MWT distance
Changes in 6MWT in patients with attenuated MPS II were significantly greater in the 0.5 mg/kg (P=0.003) and 1.0 mg/kg (P=0.015) idursulfase-β groups than in the active comparator group.
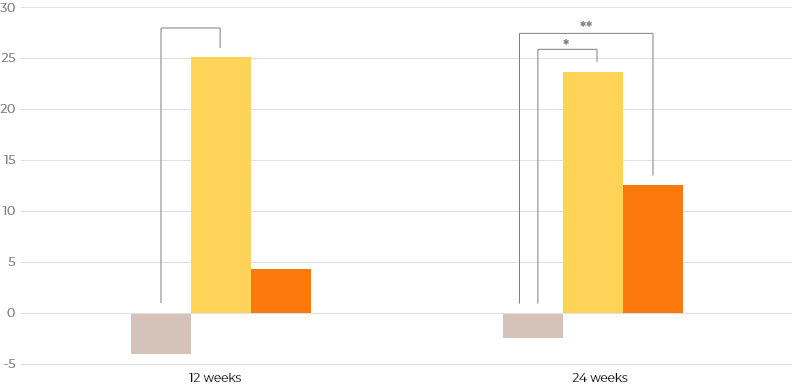
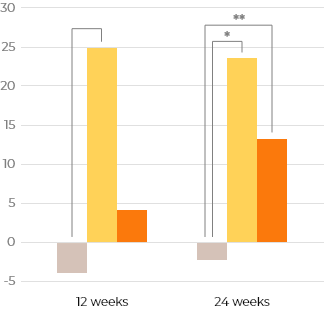
Changes of secondary efficacy variables from baseline to 24 weeks
Idursulfase-β showed similar effectiveness to the active comparator in FVC, echocardiography, and joint range of motion.
0.5 mg/kg/week (N)
0.5 mg/kg/week (N)
1.0 mg/kg/week (N)
0.5 mg/kg/week (N)
0.5 mg/kg/week (N)
1.0 mg/kg/week (N)
Safety Information
Precautions
Storage And
Shelf-life
- Store at a 2 ºC to a 8 ºC in a hermetic container.
- The shelf-life of this product is 36 months from the date of manufacture.
Adverse
Reactions
- All adverse reactions in patients treated with Hunterase weekly for 24 weeks compared with the active comparator during the clinical trial are shown in the pdf file below. 3 serious adverse reactions were observed: 2 cases of otitis media and 1 case of gastroenteritis. However, all cases were determined as ‘not-related’ to Hunterase.
- Adverse reactions associated with Hunterase were urticaria, rashes, and pruritus.
All adverse reactions were mild and controlled by adjusting the infusion rate and using proper drug treatments.
ENG Package Insert
How to Use
Recommended dosage
- Method: intravenous infusion, once weekly.
- Each vial of Hunterase contains 2 mg/ml of Idursulfase-β.
One vial contains 6 mg of Idursulfase-β in 3 ml solution and is for single use only. - Recommended dosage of Idursulfase-β protein = Patient’s weight (kg) * 0.5 mg/kg
Automatic calculation
Enter your weight and it will be calculated automatically.
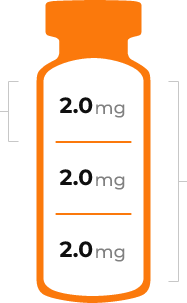
Idursulfase-ß 6.0 mg / 3 mL
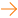
Injection Process
This information is based on the common clinical practice. It is not published or written in the package insert.
Recommendation
The initial infusion rate for the first 15 minutes – 8 mL/hr. If the infusion is well tolerated, the rate may be increased by 8 mL/hr increments every 15 minutes. The infusion rate should not exceed 100 mL/hr.Precautions in Storage and Handling
- Store Hunterase vials under refrigeration at 2 ºC to 8 ºC
- Protect from light without freezing and do not shake it.
- Do not use Hunterase after the expiration date on the vial.
- This product contains no preservatives. The diluted solution should be used immediately. If immediate use is not possible, the diluted solution can be stored refrigerated at 2 ºC to 8 ºC for up to 48 hours, or must be administered within 8 hours if held at room temperature.
- Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:42
- Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021;21:67-75
- Mol Genet Metab. 2015;114(2):156-60